Serpstack API Documentation
The serpstack API was built to offer a way of scraping Google SERP data in real-time and at scale. Implementation takes just a few minutes using the simple HTTP GET URL structure, and results are returned in JSON or CSV.
This documentation will outline in detail specifications, access and available API endpoints. At the very bottom you will find code samples in different programming languages. In case any technical questions are left unanswered, please feel free to contact serpstack Customer Service for assistance.
API Access Key & Authentication
After signing up for an account, each user will be assigned a unique API access key. This key will be used to authenticate with the API via HTTP GET and access any of the available endpoints.
To authenticate with the API, simply append your API access key to the API's base URL using the access_key parameter.
Sign Up to Run API Requesthttps://api.serpstack.com/search ? access_key = YOUR_ACCESS_KEY
Keep your key safe: To prevent unauthorized use of your account or API access, please make sure to keep your API access key private and safe from third parties. Your access key can be reset with immediate effect in your account dashboard.
256-bit HTTPS Encryption Available on: All Plans
Customers subscribed to any plan can connect to the API using industry standard HTTPS (SSL) by appending an s to the HTTP Protocol. Please find an example API request using HTTPS below.
Example API Request:
https://api.serpstack.com/search
API Error Codes
If an API request fails, a JSON object containing details about the error will be returned by the API. Find below an example error that is returned if the maximum allowed API request limit has been reached or exceeded.
Example Error:
{
"success": false,
"error": {
"code": 104,
"type": "usage_limit_reached",
"info": "Your monthly API request volume has been reached. Please upgrade your plan."
}
}
Common API Errors:
| Code | Type | Info |
|---|---|---|
404 |
404_not_found |
User requested a resource which does not exist. |
101 |
missing_access_key |
User did not provide an access key. |
101 |
invalid_access_key |
User provided an invalid access key. |
102 |
inactive_user |
User account is inactive or blocked. |
103 |
invalid_api_function |
User requested a non-existent API function. |
104 |
usage_limit_reached |
User has reached his subscription's monthly request allowance. |
105 |
function_access_restricted |
The user's current subscription does not support this API function. |
105 |
https_access_restricted |
The user's current subscription plan does not support HTTPS. |
210 |
missing_location_query |
User has not provided a valid location value inside the query parameter. For details, please refer to the Locations API section of this documentation. |
310 |
missing_search_query |
User has not provided a valid value inside the query parameter. |
311 |
invalid_engine |
User has provided an invalid value inside the query parameter. |
312 |
invalid_output_type |
User has provided an invalid value inside the output parameter. |
313 |
empty_field_list |
User has not provided a valid value inside the csv_list parameter. |
314 |
invalid_search_type |
User has not provided a valid value inside the type parameter. |
315 |
invalid_google_domain |
User has not provided a valid Google domain inside the google_domain parameter. |
316 |
invalid_time_period |
User has not provided a valid value inside the period parameter. |
317 |
missing_start_date |
User has not provided a valid date inside the period_start parameter. |
318 |
missing_end_date |
User has not provided a valid date inside the period_end parameter. |
319 |
invalid_start_date |
User has provided an invalid date inside the period_start parameter. |
320 |
invalid_end_date |
User has provided an invalid date inside the period_end parameter. |
321 |
invalid_sort_type |
User has provided an invalid value inside the sort parameter. |
322 |
invalid_images_page |
User has provided an invalid value inside the images_page parameter. |
323 |
invalid_images_color |
User has provided an invalid value inside the images_color parameter. |
324 |
invalid_images_size |
User has provided an invalid value inside the images_size parameter. |
325 |
invalid_images_type |
User has provided an invalid value inside the images_type parameter. |
326 |
invalid_images_usage |
User has provided an invalid value inside the images_usage parameter. |
327 |
request_failed |
API request failed due to an unknown error. Please contact customer support and report the error. |
Google Search API Available on: All plans
API Request & Parameters
If not otherwise specified, the serpstack API will always default to delivering search results from Google. To query the API for Google search results, simply append the query parameter to the API's base URL and set it to a search query of your choice.
Example API Request:
Sign Up to Run API Requesthttps://api.serpstack.com/search ? access_key = YOUR_ACCESS_KEY & query = mcdonalds
HTTP GET Request Parameters:
| Object | Description |
|---|---|
access_key |
[Required] Your API access key, available in your account dashboard. |
query |
[Required] Specify any query to search for. (Advanced operators like intext: are supported) |
engine |
[optional] Specify which search engine to use: google (default) |
type |
[optional] Specify which Google category to search: web (default) for standard web search, images, videos, news or shopping |
device |
[optional] Specify which device to use: desktop (default), mobile or tablet |
location |
[optional] Specify a geographic location for your query to be processed from, either using free-text or by making a request to the Locations API endpoint and using the canonical_name response object. |
auto_location |
[optional] Set this parameter to 1 (on, default) or google_domain, gl and hl based on the specified location. |
google_domain |
[optional] Specify a Google domain to use for your query. (Default: google.com) Download a list of supported domains: resource.google.domains.csv |
gl |
[optional] Specify a country code to use for your query. (Default: us for United States) Download a list of supported 2-letter country codes: resource.google.countries.csv |
hl |
[optional] Specify a language to use for your query. (Default: en for English) Download a list of all supported languages: resource.google.languages.csv |
safe |
[optional] Set this parameter to 1 (on) or |
period |
[optional] Use this parameter to filter search results based on a specific time period. Possible values: last_hour, last_day, last_week, last_month, last_year or custom. |
period_start |
[optional] If the period parameter is set to custom, you can use this parameter to specify a start date for your custom time period. (Format: YYYY-MM-DD) |
period_end |
[optional] If the period parameter is set to custom, you can use this parameter to specify an end date for your custom time period. (Format: YYYY-MM-DD) |
news_type |
[optional] When searching Google news, set this parameter to blogs in order to filter your results to blog-related results only. (Default: all) |
exclude_autocorrected_results |
[optional] Set this parameter to 1 (on) or |
images_page |
[optional] When searching Google images, set this parameter to an integer of your choice to limit the number of image results. (Example: 5) |
images_color |
[optional] When searching Google images, use this parameter to filter image results by color. Possible values: any (default), black_and_white, transparent, red, orange, yellow, green, teal, blue, purple, pink, white, gray, black or brown |
images_size |
[optional] When searching Google images, use this parameter to filter image results by image size. Possible values: large, medium or icon |
images_type |
[optional] When searching Google images, use this parameter to filter image results by image type. Possible values: clipart, line_drawing or gif |
images_usage |
[optional] When searching Google images, use this parameter to filter image results by reuse policy. Possible values: reuse_with_modification, reuse, non_commercial_reuse_with_modification or non_commercial_reuse |
sort |
[optional] If the period parameter is set to any period, you can use this parameter to sort your search results. Possible values: relevance or date. |
page |
[optional] Specify which page of results to show. (Default: 1 for the first page) |
num |
[optional] Specify the number of results to show per page. (Default: 10 - shows 10 organic results) |
output |
[optional] Specify which API response format to return: json (default) or csv. |
csv_fields |
[optional] If output is set to csv, you can use this parameter to specify which response objects should be included in your CSV file. Simply set csv_fields to one or multiple comma-separated field identifiers like search_parameters.query or organic_results.title to limit your CSV file to these fields. |
API Response & Definitions
Your API response strongly depends on your search query and the parameters you choose to make use of. Find below a representative example API response, returned for the query mcdonalds and containing some of Google's key response objects. Each available response object will be explained further below in this section.
Basic Response Objects:
| Object | Description |
|---|---|
request > success |
Returns true if your API request has succeeded. |
request > processed_timestamp |
Returns the exact UNIX timestamp for when your API request was processed by the API. |
request > search_url |
Returns the exact search URL used for your API request. |
request > total_time_taken |
Returns the total processing time of your API request. |
search_parameters > engine |
Returns the name of the search engine used for your API request. (Default: google) |
search_parameters > query |
Returns the requested search query. |
search_parameters > type |
Returns the type of Google search used for your API request. Possible values: web (default), images, videos, news, shopping |
search_parameters > device |
Returns the name of the device type used for your API request. |
search_parameters > google_domain |
Returns the Google domain used for your API request. |
search_parameters > hl |
Returns the content of the hl parameter sent along with your API request. |
search_parameters > gl |
Returns the content of the gl parameter sent along with your API request. |
search_parameters > page |
Returns the current page number as an integer. |
search_parameters > num |
Returns the specified numbers of results per page as an integer. (Default: 10) |
search_parameters > location |
Returns the location sent along with your API request. |
search_parameters > output |
Returns the output requested along with your API request. (Default: json) |
search_information > total_results |
Returns the total number of results found for your search query. |
search_information > time_taken_displayed |
Returns the total processing time displayed by the search engine. |
search_information > did_you_mean |
Returns a "did you mean" search term suggestion if Google detects a typo, misspelling or error in your query. |
search_information > showing_results_for |
Returns the actual search term Google is showing results for. (Only applicable if Google detects a typo, misspelling or error in the query you sent and knows better) |
search_information > query_displayed |
Returns the query displayed by the search engine. |
search_information > detected_location |
Returns the location name Google is displaying in the search results page footer. This response object offers a good way of making sure that your specified location is actually detected by Google. |
search_information > no_results_for_original_query |
Returns true or false depending on whether or not Google is showing results for a different search term than sent in your query. Example: If your query is mcdonalsd, Google would detect a typo and instead show results for mcdonalds. In this case, the no_results_for_original_query would return true. |
Please note: The response objects above are part of the basic result set ot the API. All other response objects are part of specific features of the API and will be explained right below.
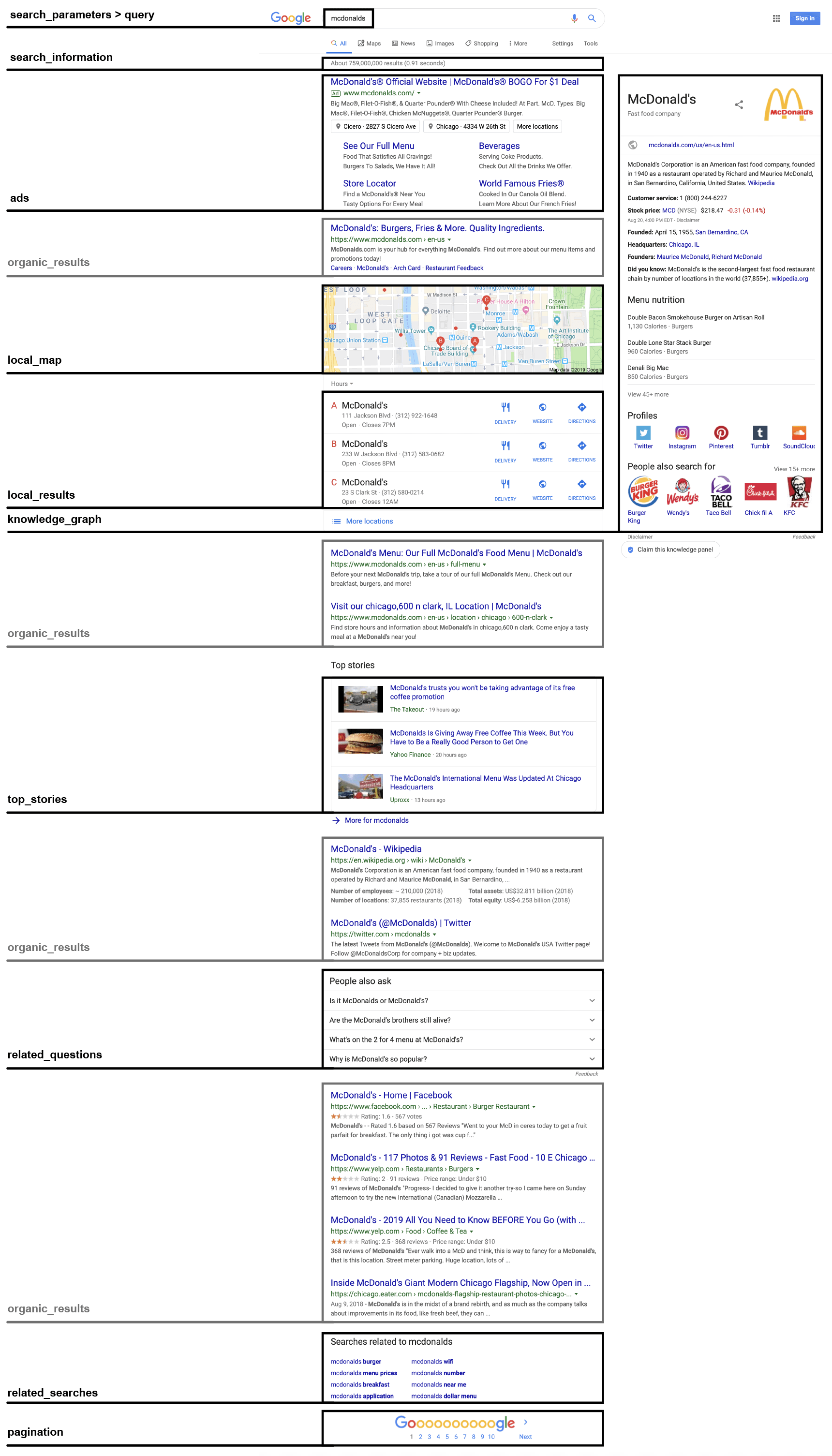
Ad Results
If Google returns any sponsored ads for your search query, the API response will come with an ads object, which contains all ads in the order they are shown in the search result. Ads can be shown either at the top or at the bottom of the search result.
Response Objects:
| Object | Description |
|---|---|
position |
Indicates the position of the respective ad in the entire block of ads. |
block_position |
Returns top or bottom depending on where the current block of ads is located in the search result. |
title |
Returns the title of the ad. |
url |
Returns the actual URL of the ad. |
tracking_url |
Returns the Google tracking URL of the ad. |
displayed_url |
Returns the displayed URL of the ad. |
domain |
Returns the domain of the ad's URL. |
description |
Returns the description of the ad. |
sitelinks |
Returns an array of links attached at the bottom of the ad, each containing: |
sitelinks > title |
Returns the title of the sitelink. |
sitelinks > url |
Returns the URL of the sitelink. |
sitelinks > tracking_url |
Returns the tracking URL of the sitelink. |
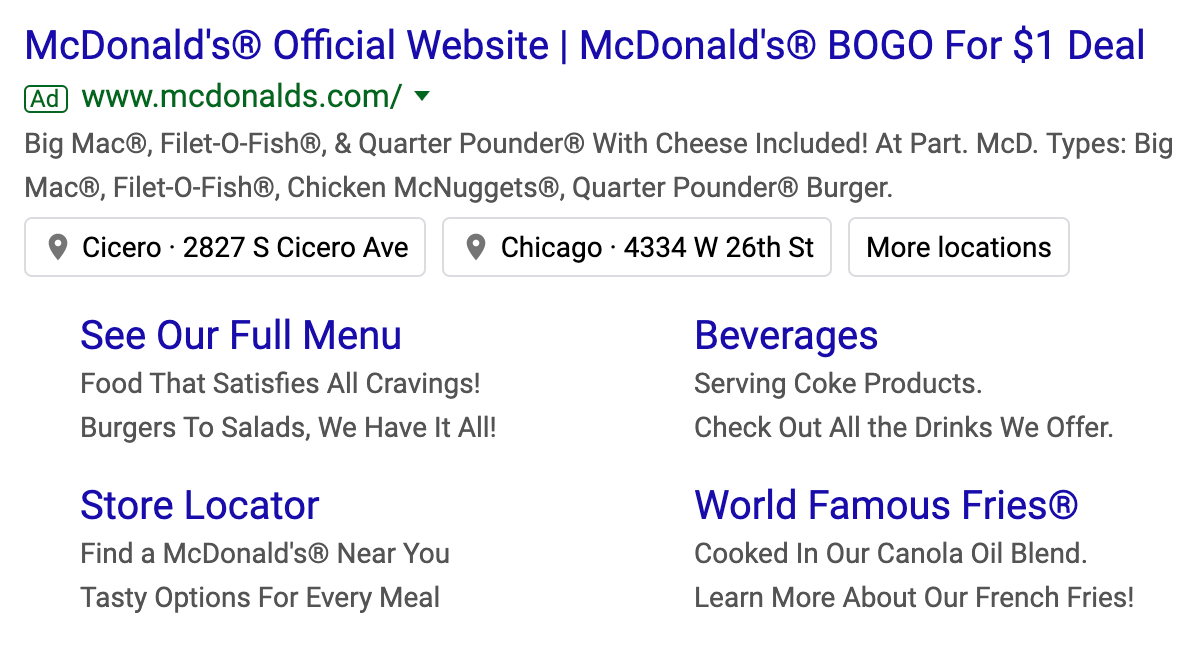
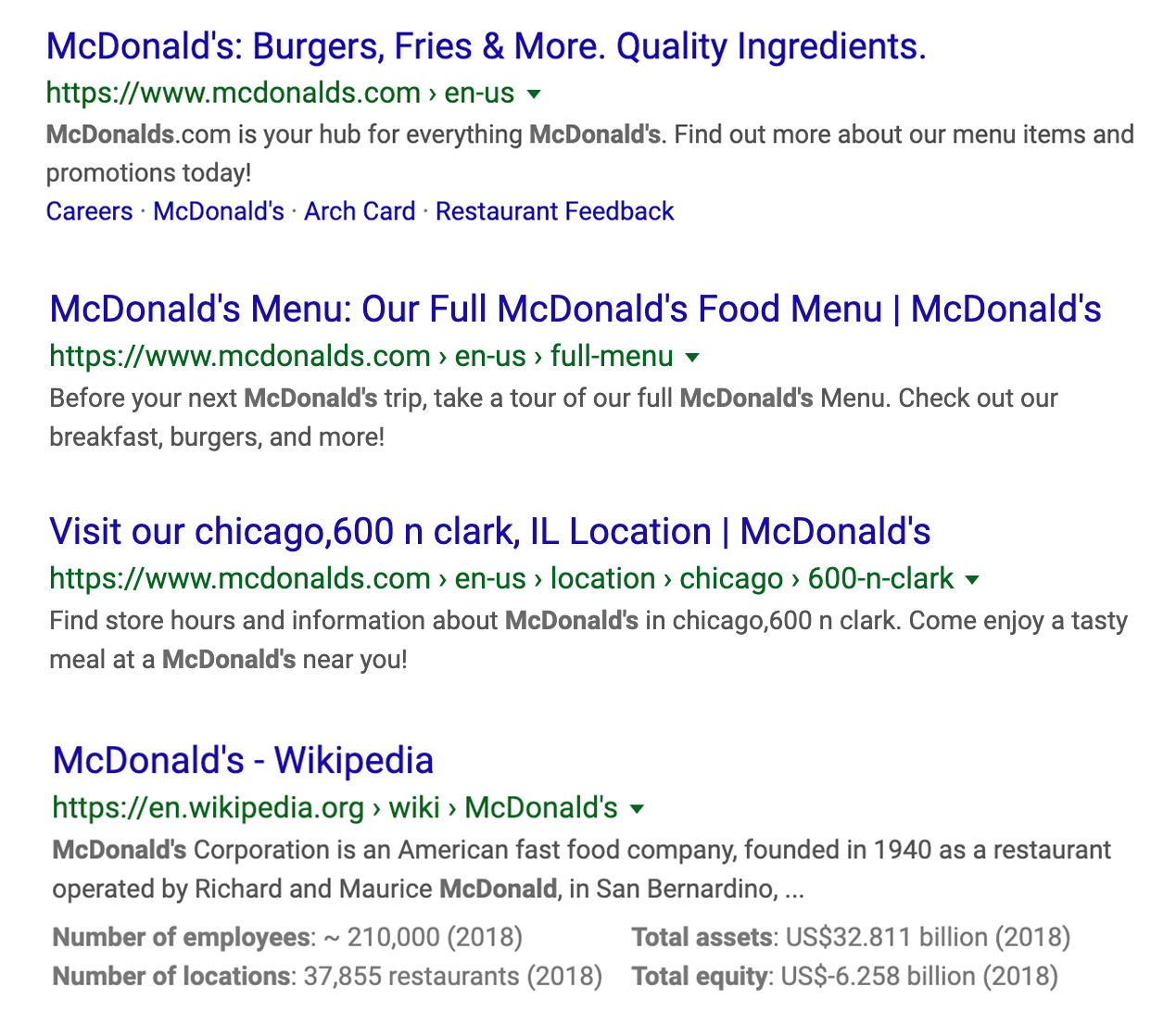
Organic Results
Organic search results are the main search results provided by Google and are determined by a series of factors, such as web traffic, back-links, social media presence, and much more. These results are parsed by the API in detail and returned as organic_results.
Response Objects:
| Object | Description |
|---|---|
position |
Returns the position of the current organic result in the entire search result. |
title |
Returns the title of the organic result. |
url |
Returns the actual URL of the organic result. |
domain |
Returns the domain of the organic result. |
displayed_url |
Returns the displayed URL of the organic result. |
snippet |
Returns the description of the organic result. |
sitelinks |
Returns all sitelinks attached at the bottom of the organic result, either as inline results (small sitelinks in a row) or expanded results (larger sitelinks below and next to each other). |
cached_page_url |
Returns a Google URL leading to the current organic result as a cached web page. |
related_pages_url |
Returns a Google URL leading to other search results related to the current organic result. |
prerender |
Returns true or false depending on whether or not the given organic result was pre-rendered. Learn about pre-rendered results here. |
rich_snippet |
Returns an array of data related to the current organic result's rich snippet, which usually contains ratings, prices, availability or additional product details. |
rich_snippet > top/bottom |
Returns top or bottom depending on where the rich snippet is located. |
rich_snippet > detected_extensions |
Returns an array of rich snippet details the API was able to identify (e.g. number of employees). |
rich_snippet > extensions |
Returns an array containing all rich snippet details as key-value pairs. |
Image Results
There are two options images can be returned by the API:
Option 1: Inline Images
When doing a standard web search and images are provided by Google within the search results, these images are returned by the API within an inline_images array.
Response Objects:
| Object | Description |
|---|---|
block_position |
Returns the position of the inline image block in the entire search result. |
image_url |
Returns the URL leading to the inline image. |
url |
Returns the website URL associated with the inline image. |
title |
Returns the title of the inline image. |
Option 2: Image Search
If images are searched specifically, with the type parameter being set to images, images are returned as an image_results array. If images are searched specifically, the API returns 100 images by default.
Response Objects:
| Object | Description |
|---|---|
position |
Returns the position of the image in the entire search result. |
title |
Returns the title of the image. |
width |
Returns the width of the original image in pixels. |
height |
Returns the height of the original image in pixels. |
image_url |
Returns the URL leading to the image. |
type |
Returns the file type of the image. (Example: png) |
url |
Returns the website URL attached to the image. |
source |
Returns the origin domain of the image. |
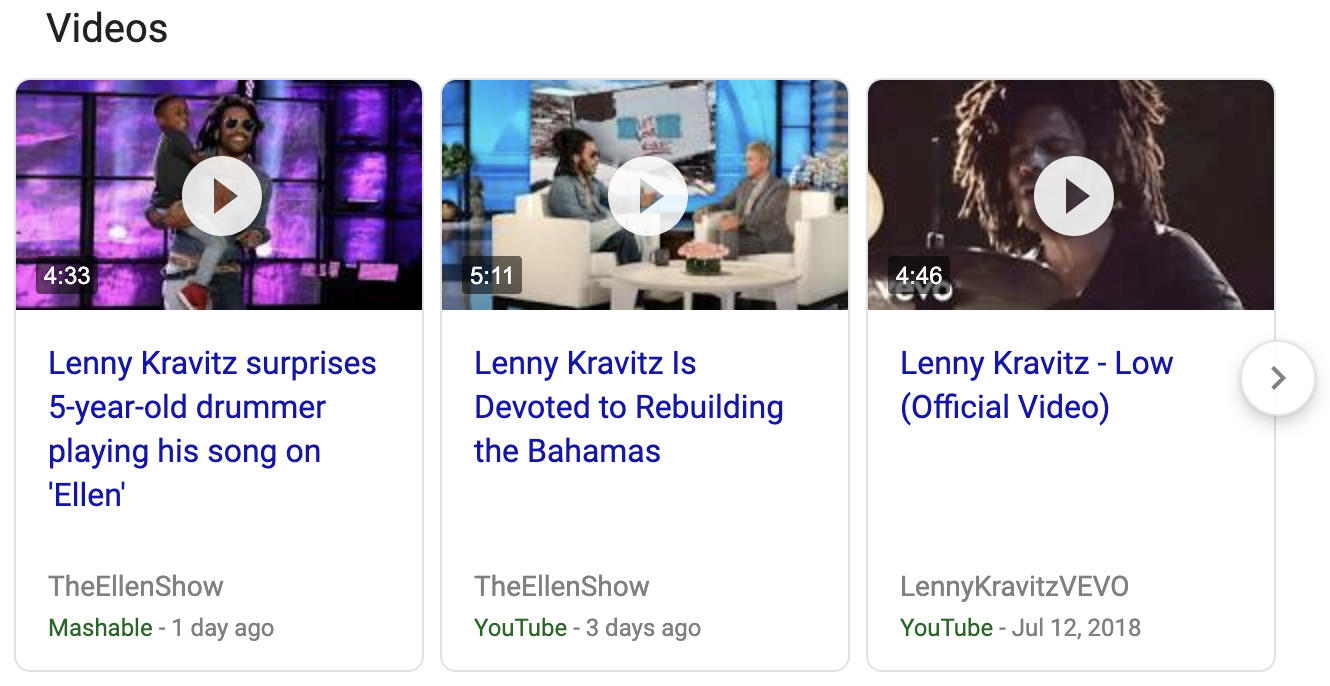
Video Results
There are two options videos can be returned by the API:
Option 1: Inline Videos
When doing a standard web search and videos are provided by Google within the search results, these videos are returned by the API within an inline_videos array.
Response Objects:
| Object | Description |
|---|---|
link |
Returns the URL of the inline video result. |
duration |
Returns the video duration in "mm:ss" format. |
duration_sec |
Returns the video duration in seconds as an integer. |
title |
Returns the title of the inline video result. |
source |
Returns the source name of the inline video result. |
author |
Returns the author of the inline video result. |
date |
Returns the upload date of the inline video result. |
image |
Returns the thumbnail image of the inline video result. |
image_url |
Returns the thumbnail image_url of the inline video result. |
rank |
Returns the rank of the inline video result on the current page. |
global_rank |
Returns the global rank of the inline video result. |
Option 2: Video Search
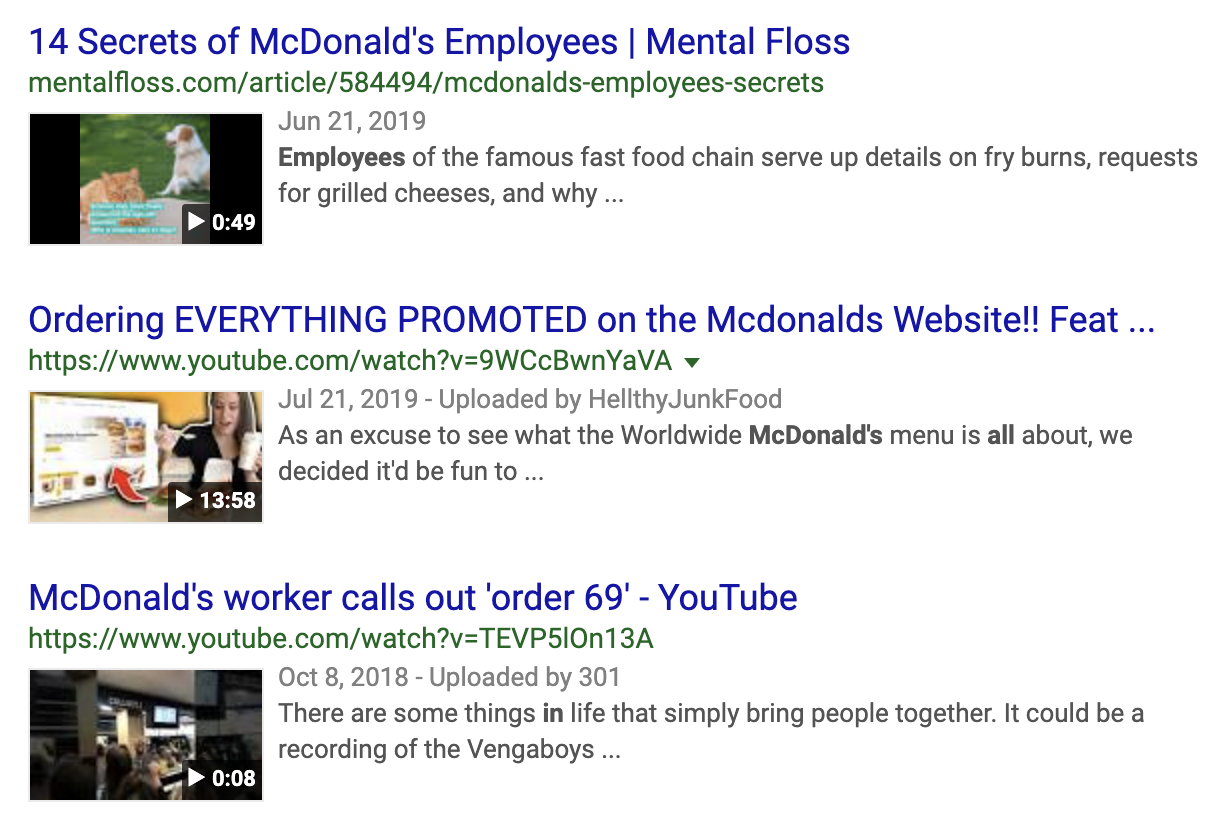
If videos are searched specifically, with the type parameter being set to videos, videos are returned as a video_results array.
Response Objects:
| Object | Description |
|---|---|
position |
Returns the position of the video result in the entire search result. |
title |
Returns the title of the video result. |
url |
Returns the URL leading to the video. |
displayed_url |
Returns the displayed URL. |
uploaded |
Returns upload date and (in some cases) uploader name. |
snippet |
Returns the video result description |
length |
Returns the length of the video in hours, minutes and seconds. (Example: 13:48 for 13 minutes and 48 seconds) |
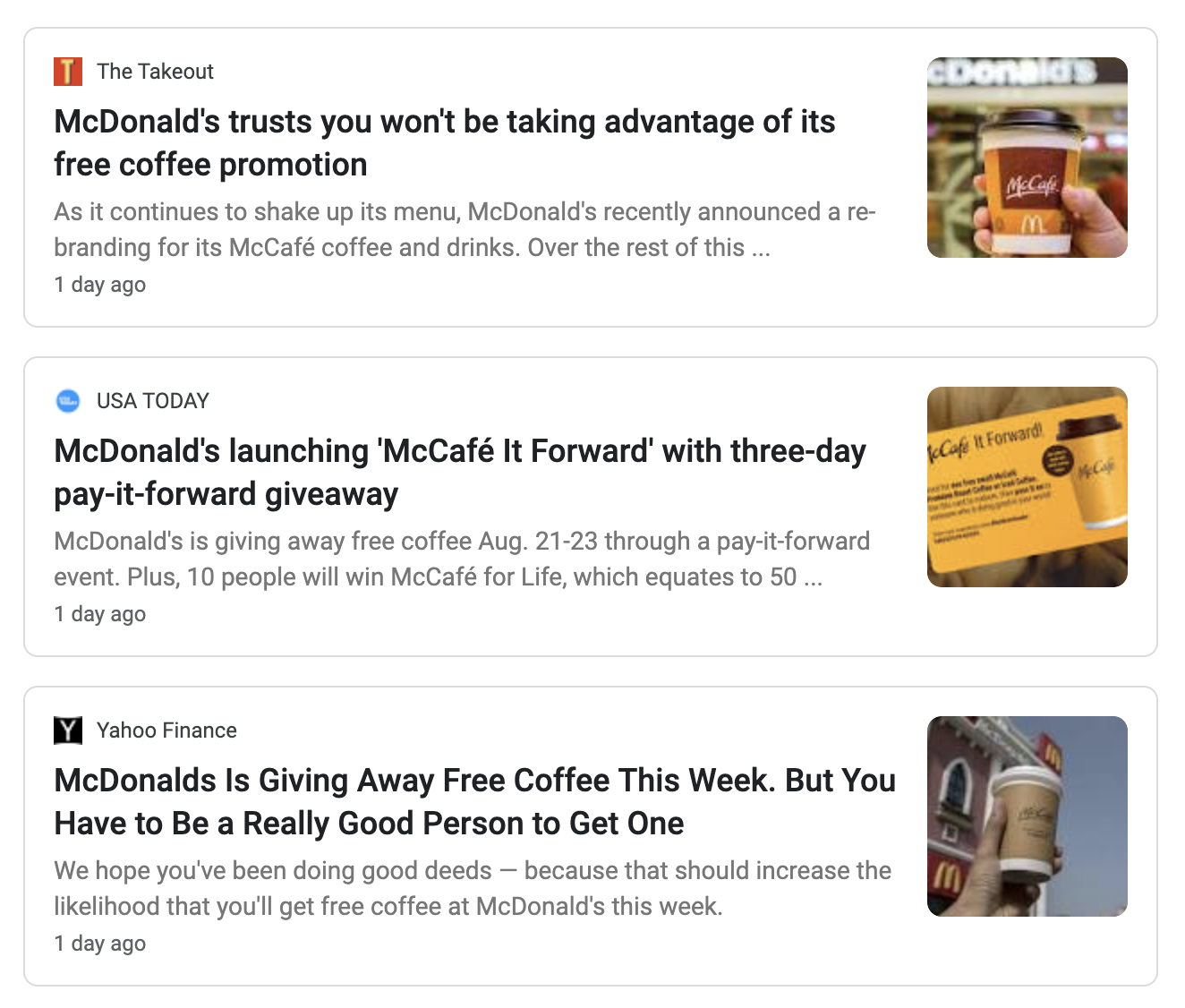
News Results
News results are returned as a news_results array only when the type parameter is set to news.
Response Objects:
| Object | Description |
|---|---|
position |
Returns the position of the news result in the entire search result. |
title |
Returns the title of the news result. |
url |
Returns the URL leading to the news article. |
source_name |
Returns the name of the news source associated with the current news result. |
uploaded |
Returns a hint on when the news result was uploaded relative to the current time. (Example: 1 day ago) |
uploaded_utc |
Returns the exact upload date of the news result. |
snippet |
Returns the description of the news result. |
thumbnail_url |
Returns a URL leading to the thumbnail of the news result. |
Shopping Results
There are two options shopping results can be returned by the API:
Option 1: Inline Shopping
When doing a standard web search and shopping items are provided by Google within search results, these items are returned by the API in an inline_shopping array.
Response Objects:
| Object | Description |
|---|---|
position |
Returns the position of the inline shopping result as an integer in relation to the entire inline shopping list. |
url |
Returns the URL of the inline shopping result. |
title |
Returns the title of the inline shopping result. |
price |
Returns the price associated with the inline shopping result. |
merchant |
Returns the merchant name associated with the inline shopping result. |
rating |
Returns a rating associated with the shopping result. |
reviews |
Returns an integer indicating the number of reviews associated with the shopping result. |
Option 2: Shopping Search
If shopping results are searched specifically, with the type parameter being set to shopping, shopping results are returned as a shopping_results array.
Response Objects:
| Object | Description |
|---|---|
position |
Returns the position of the shopping result in the entire search result. |
title |
Returns the title of the shopping result. |
url |
Returns the URL leading to the shopping item. |
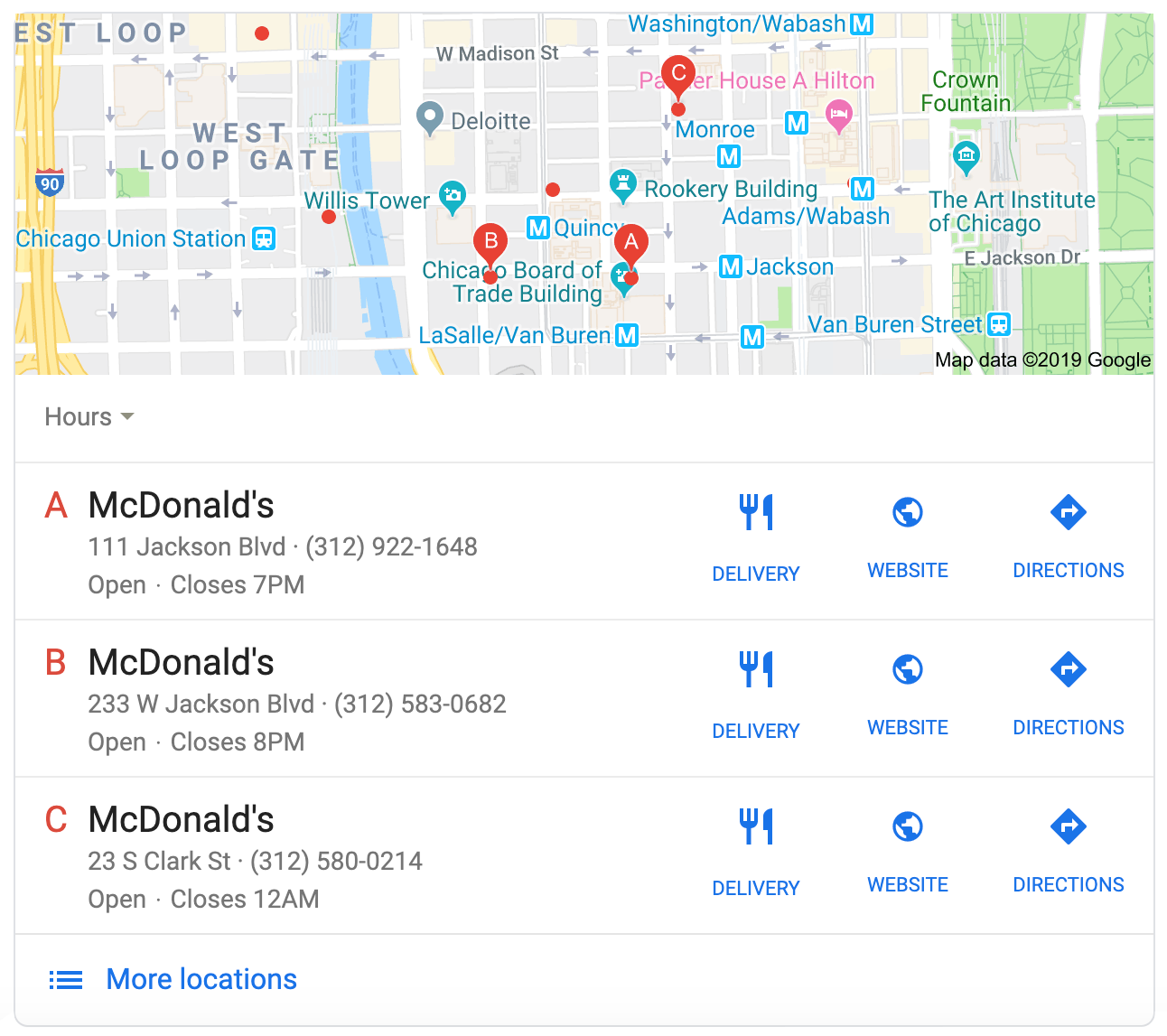
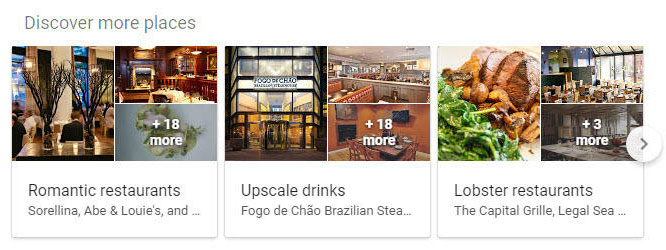
Local Results
For many searches Google returns both a local map and a series of local results below. These items are returned together in almost 100% of all cases. The API will return local map details as local_map and local results as local_results.
local_map Response Objects:
| Object | Description |
|---|---|
url |
Returns the URL of the local map result. |
coordinates > latitude |
Returns the latitude coordinate associated with the local map result. |
coordinates > longitude |
Returns the longitude coordinate associated with the local map result. |
image_url |
Returns a URL leading to the image of the local map result. |
position |
Returns the position of the local result. |
title |
Returns the title of the local result. |
image_url |
Returns the image URL of the local result, if available. |
address |
Returns the address of the local result. |
extensions |
Returns additional information about the local result, if available. |
rating |
Returns the rating of the local result, if available. |
reviews |
Returns the number of reviews for the local result, if available. |
type |
Returns the type or contact information of the local result. |
price |
Returns the price range of the local result, if available. |
local_results Response Objects:
| Object | Description |
|---|---|
position |
Returns the position of the local result in the local results block. |
title |
Returns the title of the local result. |
coordinates > latitude |
Returns the latitude coordinate associated with the local result. |
coordinates > longitude |
Returns the longitude coordinate associated with the local result. |
image_url |
Returns the image URL associated with the local result. |
address |
Returns the address associated with the local result. |
extensions |
Returns an array of additional data associated with the local result. |
rating |
Returns a rating associated with the local result. |
reviews |
Returns an integer indicating the number of reviews associated with the local result. |
type |
Returns any type of detail about the local result. (Example: phone number or opening hours) |
price |
Returns a price associated with the local result. |
url |
Returns the website URL associated with the local result. |
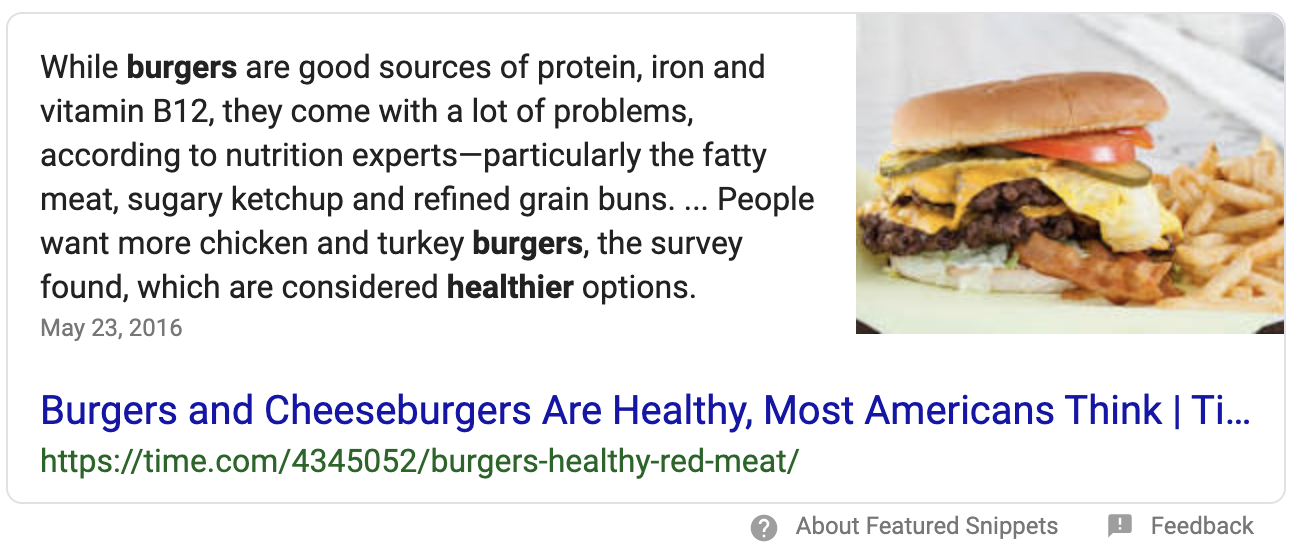
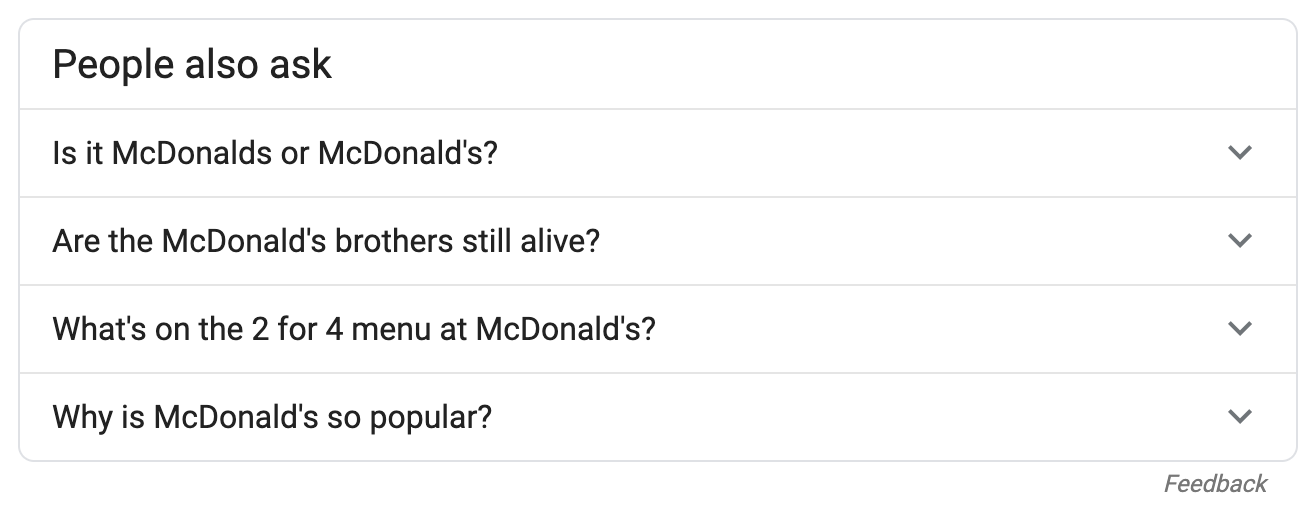
Answer Box
Google is capable of providing a large variety of direct answers to questions, from simple questions all the way to solutions of complicated mathematical formulas. The serpstack API is able to parse all of the most common formats, of which two are explained below. Answers to questions of all types will be returned by the API as an answer_box array. Please note that the answers array can contain multiple answers.
Example 1: Simple Answer
Below you will find an example API response for a simple question answered by Google.
Response Objects:
| Object | Description |
|---|---|
featured_snippets |
Returns a list of featured snippets within the answer box. |
type |
Returns the type of the featured snippet. |
display_link |
Returns the display URL of the featured snippet. |
link_title |
Returns the title of the featured snippet link. |
link |
Returns the actual URL leading to the source of the featured snippet. |
value > text |
Returns the text content of the featured snippet. |
rank |
Returns the rank of the featured snippet on the current page. |
global_rank |
Returns the global rank of the featured snippet. |
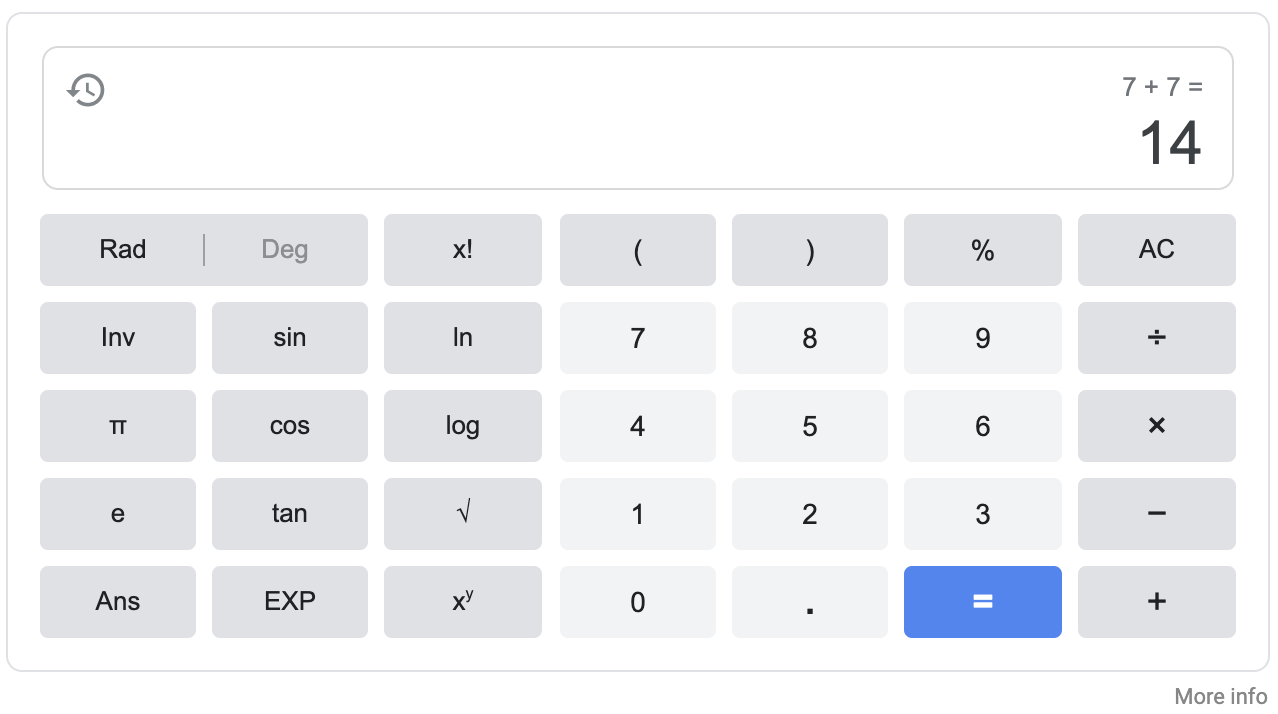
Example 2: Calculator Result
Below you will find an example API response for a question Google answers using the calculator.
Response Objects:
| Object | Description |
|---|---|
answer |
Returns the calculation result. |
type |
Returns the type of answer provided by Google. |
formula |
Returns the formula contained in the original query. |
Weather Box
If your Google search query is related to the weather in a specific location, Google will return weather information as an object called weather_box. This object contains details about current and future weather conditions in the given location.
Response Objects:
| Object | Description |
|---|---|
location |
Returns the location associated with the given weather information. |
time |
Returns the day and time associated with the current weather. |
description |
Returns a string that can be displayed to describe the current weather condition. |
weather_image |
Returns the a URL to a PNG image associated with the weather condition. |
precipitation > display |
Returns precipitation unit and value as a string to display. |
precipitation > unit |
Returns the precipitation unit as a string. |
precipitation > value |
Returns the precipitation value as an integer. |
humidity > display |
Returns humidity unit and value as a string to display. |
humidity > unit |
Returns the humidity unit as a string. |
humidity > value |
Returns the humidity value as an integer. |
temperature > display |
Returns temperature unit and value as a string to display. Unit can be celsius or fahrenheit. |
temperature > unit |
Returns the temperature unit as a string. |
temperature > value |
Returns the temperature value as an integer. |
temperature > type |
Returns the type of temperature returned. Only used in forecast data. Possible values: low or high |
wind > display |
Returns wind unit and value as a string to display. Unit can be km/h or mph. |
wind > unit |
Returns the wind unit as a string. |
wind > value |
Returns the wind value as an integer. |
day |
Returns the forecast day in 3-letter format. Example: Thu |
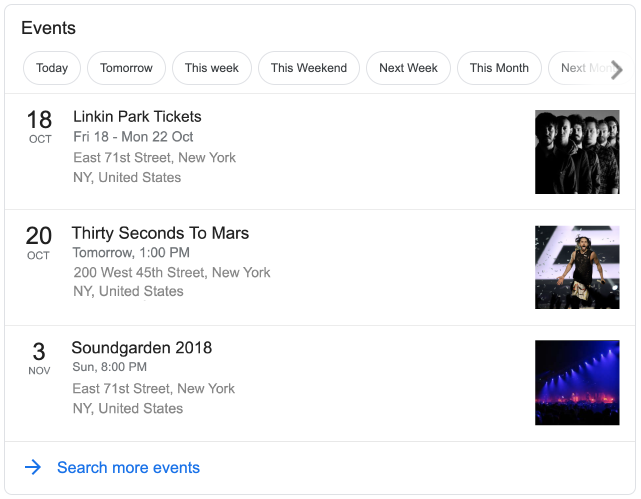
Events
If there are any events relevant to your search query, Google will show a rich snippet containing event results. These results are returned by the serpstack API as an events array.
Response Objects:
| Object | Description |
|---|---|
title |
Returns the title of the event. |
url |
Returns a Google URL leading to details of the event. |
date > day |
Returns the day of the event as an integer. |
date > month |
Returns the month of the event as a string. |
date > display |
Returns the entire date as a string to display. |
address > line1 |
Returns the first address line. |
address > line2 |
Returns the second address line. |
image_url |
Returns a URL leading to the cached event image. |
block_position |
Returns the position of the inline events block in the entire search result. |
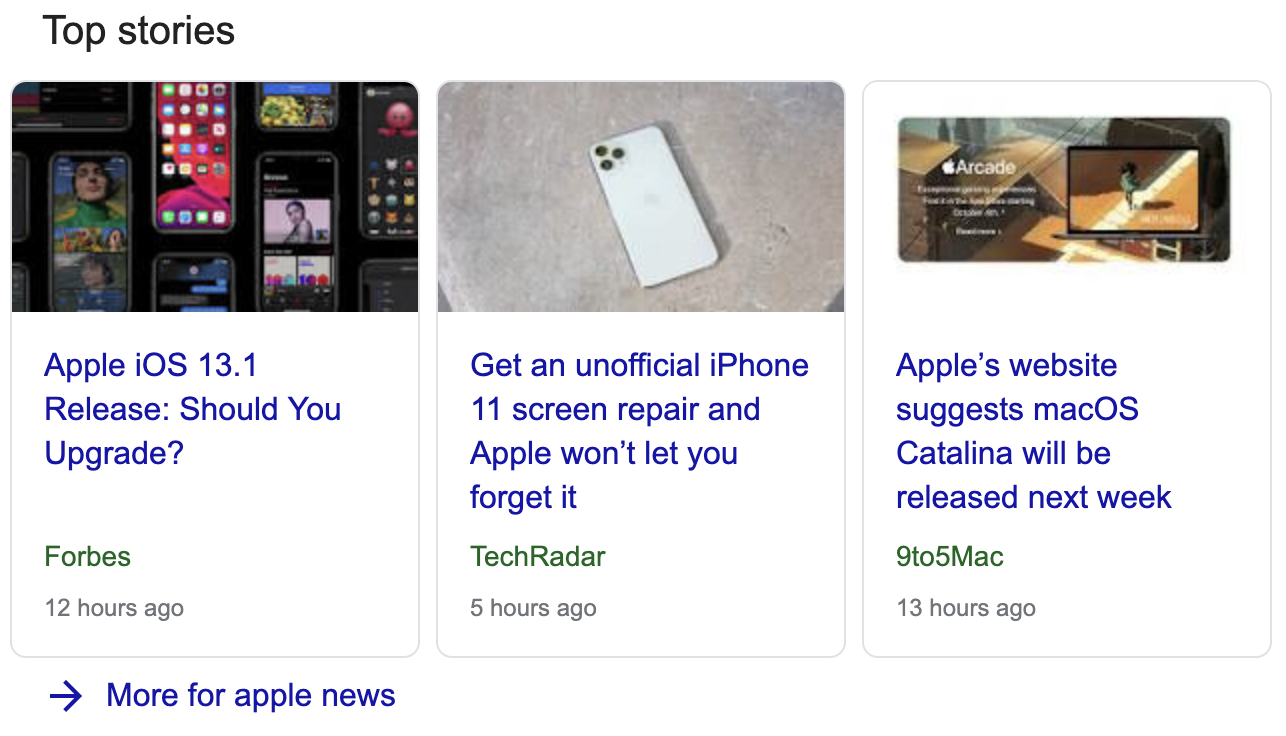
Top Stories
If there are any trending news stories relevant to your search query, Google will return those in a section called "Top Stories". This section is returned by the API as a top_stories array.
Response Objects:
| Object | Description |
|---|---|
block_position |
Returns the position of the inline image block in the entire search result. |
url |
Returns a URL to the given top story. |
title |
Returns the title of the given top story. |
source |
Returns source name of the given top story. |
uploaded |
Returns the upload date of the given story. |
uploaded_utc |
Returns the upload date (UTC) of the given story. |
Knowledge Graph
A Knowledge Graph is returned by Google whenever there is enough imformation about the search query from Google directly or from informational sources, such as Wikipedia. Knowledge Graphs will be returned in a knowledge_graph object by the API.
Response Objects:
| Object | Description |
|---|---|
title |
Returns the title of the Knowledge Graph. |
type |
Returns any type of detail about the topic in the Knowledge Graph. (Example: Fast food company) |
image_urls |
Returns an array of image URLs leading to images associated with the Knowledge Graph. |
description |
Returns the description of the Knowledge Graph. |
source > name |
Returns the name of the source the information contained in the Knowledge Graph is sourced from. |
source > url |
Returns the URL of the source the information contained in the Knowledge Graph is sourced from. |
website |
Returns the website URL associated with the topic in the Knowledge Graph. |
founded |
Returns the date and location the company in the Knowledge Graph was founded in. (This is a response object specific to company information and is not always returned.) |
headquarters |
Returns the address of the headquarters of the company in the Knowledge Graph. (This is a response object specific to company information and is not always returned.) |
founders |
Returns an array of names of founders of the company in the Knowledge Graph. (This is a response object specific to company information and is not always returned.) |
subsidiaries |
Returns an array of names and URLs of subsidiaries of the company in the Knowledge Graph. (This is a response object specific to company information and is not always returned.) |
did_you_know |
Returns an additional information text about the topic in the Knowledge Graph. |
profiles |
Returns an array containing names and URLs of social profiles related to the topic in the Knowledge Graph. |
people_also_search_for |
Returns an array containing names and URLs of topics related to the topic in the Knowledge Graph. |
Please note: While the example above shows the most type of Knowledge Graph, please note that there are multiple types of information a Knowledge Graph contain. Not all possible API response objects are covered by this documentation at this point.
Pagination
The API does not stop at page 1 of Google, the upcoming nine pages are listed along with URLs in the API's pagination response object.
Response Objects:
| Object | Description |
|---|---|
current_page |
Returns the current page as an integer. |
next_page |
Returns the number of the next page as an integer. |
next_page_start |
Returns the start index for the next page. |
next_page_link |
Returns the URL leading to the next page. |
pages |
Returns the pagination information for upcoming pages, each containing the page number, start index, and link. |
Locations API
There is a dedicated API endpoint that you can use to look up supported locations based on a query string. The purpose of this API endpoint is to give you a way of specifying the exact location you would like to use when making a request to the search endpoint.
Request & Response
To look up a location, simply use the API's locations endpoint and append your search query using the query parameter. By default, the API will return the 10 results that come closest to your query. You can manually force the API to return more results by setting the limit parameter to an integer of your choice, but a maximum of 50.
Example API Request:
Sign Up to Run API Requesthttps://api.serpstack.com/locations ? access_key = YOUR_ACCESS_KEY & query = new york
HTTP GET Request Parameters:
| Object | Description |
|---|---|
access_key |
[Required] Your API access key, available in your account dashboard. |
query |
[Required] Specify your location query. | limit |
[optional] Specify the number of matching locations the API should return. (Default: 10) |
Example API Response:
If matching locations were found, the serpstack API will return each location found as a separate array object containing a series of identifiers associated with the respective location object.
[
{
"name": "New York",
"canonical_name": "New York,New York,United States",
"country_code": "US",
"target_type": "City",
"reach": 23600000,
"latitude": -74.0059413,
"longitude": 40.7127837
},
{
"name": "New York, NY",
"canonical_name": "New York,NY,United States",
"country_code": "US",
"target_type": "DMA Region",
"reach": 23600000,
"latitude": -74.0059413,
"longitude": 40.7127837
},
{
"name": "New York",
"canonical_name": "New York,United States",
"country_code": "US",
"target_type": "State",
"reach": 23600000,
"latitude": -74.0059413,
"longitude": 40.7127837
},
{
"name": "Bronx County",
"canonical_name": "Bronx County,New York,United States",
"country_code": "US",
"target_type": "County",
"reach": 23600000,
"latitude": -73.8648268,
"longitude": 40.8447819
},
{
"name": "Kings County",
"canonical_name": "Kings County,New York,United States",
"country_code": "US",
"target_type": "County",
"reach": 23600000,
"latitude": -73.9441579,
"longitude": 40.6781784
}
]
API Response Objects:
| Response Object | Description |
|---|---|
name |
Returns the name of the matching location |
canonical_name |
Returns the canonical name of the matching location. Use this object to specify your location when making requests to the search endpoint. |
country_code |
Returns the 2-letter country code associated with the matching location. |
target_type |
Returns the location type. Possible values: City, County, State, DMA Region, Neighborhood, Province, Department, District |
reach |
Returns the number of people the matching location will reach on Google. |
latitude |
Returns the latitude coordinate associated with the matching location. |
latitude |
Returns the longitude coordinate associated with the matching location. |
Code Examples
Below you will find code examples that print the total number of search results as well as each organic search result returned by the serpstack API. The API is compatible with any programming language available, below we are including example code for PHP, Python, Nodejs, jQuery, Go and Ruby.
Code Example - PHP
$queryString = http_build_query([
'access_key' => 'YOUR_ACCESS_KEY',
'query' => 'mcdonalds',
]);
$ch = curl_init(sprintf('%s?%s', 'https://api.serpstack.com/search', $queryString));
curl_setopt($ch, CURLOPT_RETURNTRANSFER, true);
$json = curl_exec($ch);
curl_close($ch);
$api_result = json_decode($json, true);
echo "Total results: ", $api_result['search_information']['total_results'], PHP_EOL;
foreach ($api_result['organic_results'] as $number => $result) {
echo "{$number}. {$result['title']}", PHP_EOL;
}
Code Example - Python
import requests
params = {
'access_key': 'YOUR_ACCESS_KEY',
'query': 'mcdonalds'
}
api_result = requests.get('https://api.serpstack.com/search', params)
api_response = api_result.json()
print "Total results: ", api_response['search_information']['total_results']
for number, result in enumerate(api_response['organic_results'], start=1):
print "%s. %s" % (number, result['title'])
Code Example - Nodejs
const axios = require('axios');
const params = {
access_key: 'YOUR_ACCESS_KEY',
query: 'mcdonalds'
}
axios.get('http://127.0.0.1:8000/serp.php', {params})
.then(response => {
const apiResponse = response.data;
console.log("Total results: ", apiResponse.search_information.total_results);
apiResponse.organic_results.map((result, number) =>
console.log(`${number+1}. ${result.title}`));
}).catch(error => {
console.log(error);
});
Code Example - jQuery
$.ajax({
url: 'https://api.serpstack.com/search',
data: {
access_key: 'YOUR_ACCESS_KEY',
query: 'mcdonalds'
},
dataType: 'json',
success: function(apiResponse) {
console.log("Total results:", apiResponse.search_information.total_results);
apiResponse.organic_results.map(function(result, number) {
console.log(number + 1 + ".", result.title);
});
}
});
Code Example - Go
package main
import (
"encoding/json"
"fmt"
"net/http"
)
type SearchInformation struct {
TotalResults int `json:"total_results"`
}
type OrganicResult struct {
Title string `json:"title"`
}
type Response struct {
SearchInformation SearchInformation `json:"search_information"`
OrganicResults []OrganicResult `json:"organic_results"`
}
func main() {
httpClient := http.Client{}
req, err := http.NewRequest("GET", "https://api.serpstack.com/search", nil)
if err != nil {
panic(err)
}
q := req.URL.Query()
q.Add("access_key", "YOUR_ACCESS_KEY")
q.Add("query", "macdonalds")
req.URL.RawQuery = q.Encode()
res, err := httpClient.Do(req)
if err != nil {
panic(err)
}
defer res.Body.Close()
var apiResponse Response
json.NewDecoder(res.Body).Decode(&apiResponse)
fmt.Println("Total results:", apiResponse.SearchInformation.TotalResults)
for index, result := range apiResponse.OrganicResults {
fmt.Printf("%d. %s\n", index + 1, result.Title)
}
}
Code Example - Ruby
require 'net/http'
require 'json'
params = {
:access_key => "YOUR_ACCESS_KEY",
:query => "mcdonalds"
}
uri = URI('https://api.serpstack.com/search')
uri.query = URI.encode_www_form(params)
json = Net::HTTP.get(uri)
api_response = JSON.parse(json)
puts "Total results: #{api_response['search_information']['total_results']}"
api_response['organic_results'].each_with_index do |result, number|
puts "#{number + 1}. #{result['title']}"
end
Business Continuity - API Overages
Ensuring our customers achieve success is paramount to what we do at APILayer. For this reason, we will be rolling out our Business Continuity plan guaranteeing your end users will never see a drop in coverage. Every plan has a certain amount of API calls that you can make in the given month. However, we would never want to cut your traffic or impact user experience negatively for your website or application in case you get more traffic.
What is an overage?
An overage occurs when you go over a quota for your API plan. When you reach your API calls limit, we will charge you a small amount for each new API call so we can make sure there will be no disruption in the service we provide to you and your website or application can continue running smoothly.
Prices for additional API calls will vary based on your plan. See table below for prices per call and example of an overage billing.
| Plan Name | Monthly Price | Number of Calls | Overage Price per call | Overage | Total price |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Basic | $29.99 | 5,000 | 0.011996 | 1,000 | $41.99 |
| Business | $99.99 | 20,000 | 0.009999 | 3,000 | $129.99 |
| Business Pro | $199.99 | 50,000 | 0.0079996 | 10,000 | $279.99 |
Why does APILayer have overage fees?
Overage fees allow developers to continue using an API once a quota limit is reached and give them time to upgrade their plan based on projected future use while ensuring API providers get paid for higher usage.
How do I know if I will be charged for overages?
When you are close to reaching your API calls limit for the month, you will receive an automatic notification (at 75%, 90% and 100% of your monthly quota). However, it is your responsibility to review and monitor for the plan’s usage limitations. You are required to keep track of your quota usage to prevent overages. You can do this by tracking the number of API calls you make and checking the dashboard for up-to-date usage statistics.
How will I be charged for my API subscription?
You will be charged for your monthly subscription plan, plus any overage fees applied. Your credit card will be billed after the billing period has ended.
What happens if I don’t have any overage fees?
In this case, there will be no change to your monthly invoice. Only billing cycles that incur overages will see any difference in monthly charges. The Business Continuity plan is an insurance plan to be used only if needed and guarantees your end users never see a drop in coverage from you.
What if I consistently have more API calls than my plan allows?
If your site consistently surpasses the set limits each month, you may face additional charges for the excess usage. Nevertheless, as your monthly usage reaches a certain threshold, it becomes more practical to consider upgrading to the next plan. By doing so, you ensure a smoother and more accommodating experience for your growing customer base.
I would like to upgrade my plan. How can I do that?
You can easily upgrade your plan by going to your Dashboard and selecting the new plan that would be more suitable for your business needs. Additionally, you may contact your Account Manager to discuss a custom plan if you expect a continuous increase in usage.
Introducing Platinum Support - Enterprise-grade support for APILayer
Upgrade your APIlayer subscription with our exclusive Platinum Support, an exceptional offering designed to enhance your business’ API management journey. With Platinum Support, you gain access to a host of premium features that take your support experience to a whole new level.
What does Platinum Support include?
| Standard Support | Platinum Support | |
|---|---|---|
| General review on the issue | ||
| Access to knowledge base articles | ||
| Email support communication | ||
| Regular products updates and fixes | ||
| Dedicated account team | ||
| Priority Email Support with unlimited communication | ||
| Priority bug and review updates | ||
| Option for quarterly briefing call with product Management | ||
| Features requests as priority roadmap input into product |
Priority Email Support: Experience unrivaled responsiveness with our priority email support. Rest assured that your inquiries receive top-priority attention, ensuring swift resolutions to any issues.
Unlimited Communication: Communication is key, and with Platinum Support, you enjoy unlimited access to our support team. No matter how complex your challenges are, our experts are here to assist you every step of the way.
Priority Bug Review and Fixes: Bugs can be a headache, but not with Platinum Support. Benefit from accelerated bug review and fixes, minimizing disruptions and maximizing your API performance.
Dedicated Account Team: We understand the value of personalized attention. That's why Platinum Support grants you a dedicated account team, ready to cater to your specific needs and provide tailored solutions.
Quarterly Briefing Call with Product Team: Stay in the loop with the latest updates and insights from our Product team. Engage in a quarterly briefing call to discuss new features, enhancements, and upcoming developments.
Priority Roadmap Input: Your input matters! As a Platinum Support subscriber, your feature requests receive top priority, shaping our product roadmap to align with your evolving requirements.
Don't settle for the standard when you can experience the exceptional. Upgrade to Platinum Support today and supercharge your APIlayer experience!